ADVERTISEMENT
What Really Happens After Gallbladder Removal?
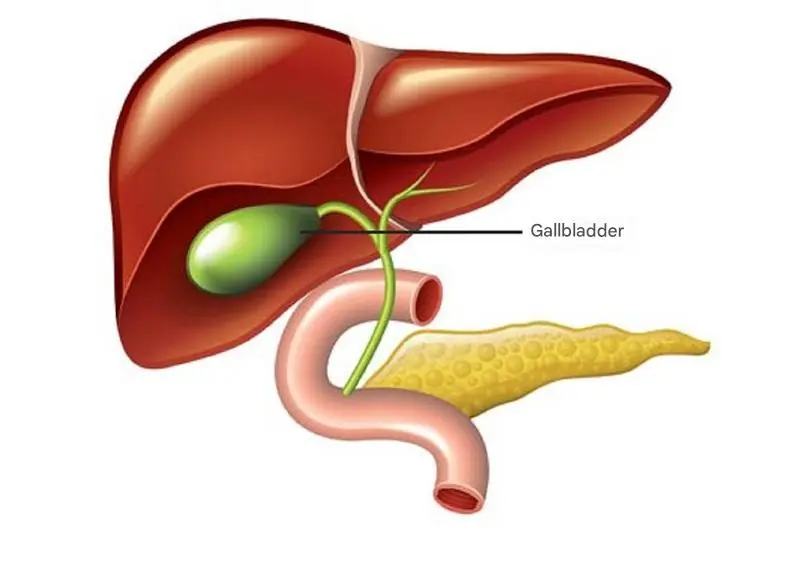
The gallbladder is a small but essential organ located beneath the liver, connected via the bile duct. Its main role is storing bile, a fluid crucial for digesting fats and maintaining digestive health.
When we eat, the gallbladder contracts and releases bile into the small intestine, helping digest fatty foods and neutralizing harmful bacteria. Problems in the gallbladder, such as gallstones, can disrupt this process, causing severe abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting. Protecting gallbladder health is therefore essential.
Should You Remove Your Gallbladder if Gallstones Are Found?
The decision to remove the gallbladder depends on the type and severity of gallstones. Small, symptomless stones typically require no surgery and can be managed conservatively. However, larger stones or those causing inflammation (cholecystitis), infection (cholangitis), or severe pain might necessitate removal.
How Your Body Changes After Gallbladder Removal
Removing the gallbladder (cholecystectomy) alters digestive processes and affects overall health:
1. Reduced Ability to Digest Fats
Without the gallbladder to store bile, your body releases bile continuously rather than in response to meals. This makes fat digestion and absorption more challenging.
2. Digestive Discomfort
Continuous bile flow can lead to indigestion, bloating, and frequent belching. The digestive system struggles to break down certain foods, especially fatty or greasy ones.
3. Disruption of Gut Bacteria
Bile contains antibacterial compounds essential for maintaining gut health. The absence of the gallbladder may disrupt the normal gut flora balance, increasing susceptibility to intestinal inflammation or infections.
4. Increased Risk of Bile Reflux
Without regulated bile release, bile might flow backward into the stomach, causing discomfort or reflux. Symptoms may include nausea, stomach pain, and heartburn.
👇 To continue reading, scroll down and click Next 👇
ADVERTISEMENT